Use of Adalimumab, a TNF-Alpha Inhibitor, is Associated with Paradoxical Psoriasis: Two Clinical Case Reports
Conteúdo do artigo principal
Resumo
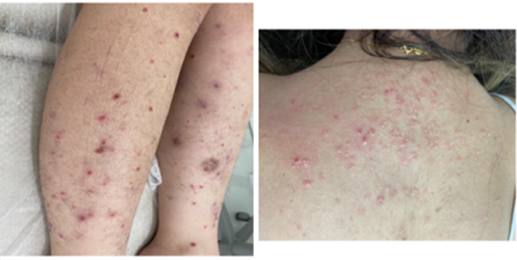
The use of tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) antagonists has become a practice applied in the treatment of various inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis. However, the use of Anti-TNF can, paradoxically, trigger side effects as a form of psoriasiform or worsening of pre-existing symptoms, in patients with or without previously diagnosed psoriasis. In view of this, two case reports were described. First, we described a 21-year-old female patient who used adalimumab for four months due to extensive suppurative hidradenitis. In the second case, we related a 32-year-old male patient diagnosed with severe Crohn's disease, with Adalimumab for three months developed psoriasis.
Detalhes do artigo

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the journal the right of first publication under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license, which allows others to share and adapt the work with proper attribution.
Referências
Wendling D, Prati C. Paradoxical effects of anti-TNF-α agents in inflammatory diseases. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2014;10(1):159–69.
Pugliese D, Guidi L, Ferraro PM, Marzo M, Felice C, Celleno L, Landi R, Andrisani G, Pizzolante F, De Vitis I, Papa A, Rapaccini GL, Armuzzi A. Paradoxical psoriasis in a large cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving treatment with anti-TNF alpha: 5-year follow-up study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Oct;42(7):880-8.
Brazilian Society of Dermatology. Brazilian Consensus on Psoriasis. Brazilian Consensus of Psoriasis 2012 Assessment and Treatment Guides. 2012;172.
Azulay-abulafia L. Imunobiológicos na Psoríase. 2009;85–96.
Harrison MJ, Dixon WG, Watson KD, King Y, Groves R, Hyrich KL, Symmons DP; British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register Control Centre Consortium; BSRBR. Rates of new-onset psoriasis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Feb;68(2):209-15.
Navarro R, Daudén E. Reacciones psoriasiformes paradójicas durante el tratamiento con terapia anti-factor de necrosis tu-moral. Manejo clínico. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(8):752–61.
Ko JM, Gottlieb AB, Kerbleski JF. Induction and exacerbation of psoriasis with TNF-blockade therapy: A review and analysis of 127 cases. J Dermatolog Treat. 2009;20(2):100–8.
Nguyen K, Vleugels RA, Velez NF, Merola JF, Qureshi AA. Psoriasiform reactions to anti-tumor necrosis factor α therapy. J Clin Rheumatol. 2013;19(7): 377–81.
Tillack C, Ehmann LM, Friedrich M, Laubender RP, Papay P, Vogelsang H, Stallhofer J, Beigel F, Bedynek A, Wetzke M, Maier H, Koburger M, Wagner J, Glas J, Diegelmann J, Koglin S, Dombrowski Y, Schauber J, Wollenberg A, Brand S. Anti-TNF an-tibody-induced psoriasiform skin lesions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease are characterised by interfer-on-γ-expressing Th1 cells and IL-17A/IL-22-expressing Th17 cells and respond to anti-IL-12/IL-23 antibody treatment. Gut. 2014 Apr;63(4):567-77.
Fania L, Morelli M, Scarponi C, Mercurio L, Scopelliti F, Cattani C, Scaglione GL, Tonanzi T, Pilla MA, Pagnanelli G, Mazzanti C, Girolomoni G, Cavani A, Madonna S, Albanesi C. Paradoxical psoriasis induced by TNF-α blockade shows immunological features typical of the early phase of psoriasis development. J Pathol Clin Res. 2020 Jan;6(1):55-68.
Xie W, Xiao S, Huang H, Zhang Z. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Paradoxical Psoriasis or Psoriasiform Lesions in In-flammatory Bowel Disease Patients Receiving Anti-TNF Therapy: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 1;13:847160.